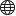
Classify As Bim Element dialog box
The Classify As Bim Element dialog box specifies the types of classification or converts the selection to a block and classifies the block reference.
- Search bar
- Bim Element categories
- Selected category elements
- Convert to block and classify the block reference
- Block name
- Search bar
- Allows you to search for an element in all listed element categories.
- Bim Element categories
- Displays all available Bim Element categories.
- Selected category elements
- Displays all the elements available for the selected category.
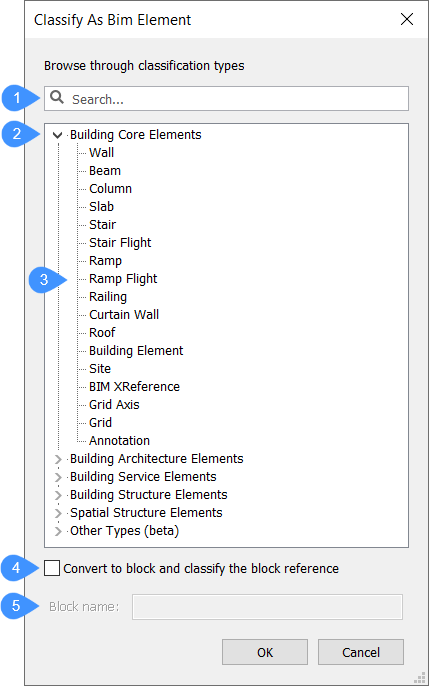
- Convert to block and classify the block reference
- Converts selection to block that then classifies as Bim Element. Selecting it enables the Block name field.
- Block name
- Allows you to enter a name for the soon to be created block reference.
Building Core Elements
- Wall
-
Vertical construction that subdivides spaces.
Example: separation wall, bearing wall, interior wall.
- Beam
-
Structural member that carries loads between or beyond points of support, usually narrow in relation to its length and (nearly) horizontal.
Example: I-beam, L-beam, T-beam, double T-beam.
- Column
-
Structural member of slender form, usually vertical, that transmits to its base the forces, primarily in compression, that are applied to it.
Example: Doric column, Ionic column, Corinthian column.
- Slab
-
Component of the construction that normally encloses a space vertically. The slab may provide the lower support (floor) or upper construction (roof slab) in any space in a building.
Example: floor slab, roof slab.
- Stair
-
Construction comprising a succession of horizontal stages (steps or landings) that make it possible to pass on foot to other levels.
Example: stairs, escalator, spiral staircases interrupted with landings.
- Stair Flight
-
Assembly of building components in a single "run" of stair steps (not interrupted by a landing). The stair steps and any stringers are included in this object.
Example: stairs, escalator, spiral staircases NOT interrupted with landings.
- Ramp
-
Inclined way or floor joining 2 surfaces at different levels.
Example: Slope/Ramp interrupted with landings.
- Ramp Flight
-
Inclined slab segment, normally providing a human circulation link between 2 landings, floors or slabs at different elevations.
Example: Slope/Ramp NOT interrupted with landings.
- Railing
-
The railing is a frame assembly adjacent to human circulation spaces and at some space boundaries where it is used instead of walls or to complement walls. It is designed to aid humans, either as an optional physical support, or to prevent injury by falling.
Example: handrail, balustrade, grab bar, guard rail.
- Curtain Wall
-
Exterior wall of a building which is an assembly of components, hung from the edge of the floor/roof structure rather than bearing on a floor.
- Roof
-
Construction enclosing the building from above.
Example: flat roof, gable roof, gambrel roof, hip roof.
- Building Element
-
The building element comprises all elements that are primarily part of the construction of a building.
Example: structural and space separating system like walls, beams, doors.
- Site
-
A defined area of land, possibly covered with water, on which the project construction is to be completed.
- BIM XReference
-
The identification of information that is not explicitly represented in the current model or in the project database. Such information may be contained in classifications, documents or libraries within the external source.
- Grid Axis
-
An individual axis that is defined in the context of a design grid. The axis definition is based on a curve of dimensionality 2.
Example: X-axis, Y-axis, Z-axis.
- Grid
-
A planar design grid defined in 3D space used as an aid in locating structural and design elements.
Example: rectangular grid, radial grid, triangular grid.
- Annotation
-
A graphical representation within the geometric context of a project, that adds a note or meaning to the objects of the project.
Example: additional line drawings, text, dimensioning, hatching, ...
Building Architecture Elements
- Window
-
Construction for closing a (near) vertical opening in a wall or pitched roof that will admit light and may admit fresh air. The window is a building element that is predominately used to provide natural light and fresh air. A window consists of a lining and one or several panels.
Example: skylights, light domes, swinging, pivoting, sliding, or revolving panels and fixed panels.
- Door
-
Construction for closing an opening. The door is a building element that is predominately used to provide controlled access for people and goods. A door consists of a lining and one or several panels.
Example: hinged, pivoted, sliding, revolving, folding doors.
- Covering
-
A covering is an element which covers some part of another element and is fully dependent on that other element.
Example: wall claddings, floorings, suspended ceilings, finish trim, base molding.
- Furnishing Element
-
Generalization of all furniture related objects.
Example: closet, table, chair, bed.
- Opening
-
Represents a void within any element that has physical manifestation.
Example: opening for a door, opening for a window.
Building Service Elements
- Distribution Control Element
-
The occurrence elements of a building automation control system that are used to impart control over elements of a distribution system. It senses elements and measures changes in the controlled variable such as temperature, humidity, pressure, or flow.
Example: thermostat
- Distribution Port
-
The occurrence of a specialized port for use within the context of distribution elements.
Example: A gas-powered hot water heater may have 3 ports: GAS, DOMESTICCOLDWATER, and DOMESTICHOTWATER. The heater is a member of 2 systems (GAS and DOMESTICCOLDWATER) and hosts 1 system (DOMESTICHOTWATER) at the corresponding port.
- Distribution Flow Element
-
The occurrence elements of a distribution system that facilitate the distribution of energy or matter, such as air, water or power.
Example: ducts, pipes, wires, fittings
- Distribution Chamber Element
-
A place at which distribution systems and their constituent elements may be inspected or through which they may travel.
Example: sump, trench
- Energy Conversion Device
-
The occurrence of a device used to perform energy conversion or heat transfer and typically participates in a flow distribution system.
Example: boiler, chiller, or a cooling coil
- Flow Fitting
-
The occurrence of a junction or transition in a flow distribution system.
Example: elbow, tee, a junction box in an electrical distribution system
- Flow Controller
-
The occurrence of elements of a distribution system that are used to regulate flow through a distribution system.
Example: damper, valve, switch, relay
- Flow Moving Device
-
The occurrence of an apparatus used to distribute, circulate or perform conveyance of fluids, including liquids and gases, and typically participates in a flow distribution system.
Example: pump, fan
- Flow Segment
-
A flow segment is a section of a distribution system that typically has only 2 ports.
Example: section of a duct, pipe, conduit, etc.
- Flow Storage Device
-
Device used for the temporary storage of a fluid such as a liquid or a gas, the voltage potential induced by the induced electron flow.
Example: tank, battery
- Flow Terminal
-
The occurrence of a permanently attached element that acts as a terminus or beginning of a distribution system. A terminal is typically a point at which a system interfaces with an external environment.
Example: air outlet, drain, water closet, sink
- Flow Treatment Device
-
Device used to change the physical properties of the medium, flow treatment types (or the instantiable subtypes) may be exchanged without being already assigned to occurrences.
Example: air, oil or water filter, duct silencer
- Flow Connection Point
-
The connection point is used to describe the geometric constraints that facilitate the physical connection of 2 objects at a point.
Building Structure Elements
- Member
-
Structural member designed to carry loads between or beyond points of support. It is not required to be load bearing. The orientation of the member (being horizontal, vertical or sloped) is not relevant to its definition.
Example: diagonal element of a truss construction
- Footing
-
A part of the foundation of a structure that spreads and transmits the load directly to the soil.
Example: wall footing, stepped footing, sloped footing, raft footing
- Pile
-
A slender timber, concrete or steel structural element, driven, jetted or otherwise embedded on end in the ground for the purpose of supporting a load. A pile is also characterized as deep foundation, where the loads are transferred to deeper subsurface layers.
Example: pile foundation
- Reinforcing Bar
-
A steel bar, usually with manufactured deformations in the surface, used in concrete and masonry construction to provide additional strength.
Example: reinforced concrete
- Reinforcing Mesh
-
A series of longitudinal and transverse wires or bars of various gauges, arranged at right angles to each other and welded at all points of intersection.
Example: reinforced concrete floor slab
- Tendon
-
A steel element used to impart pre-stress to concrete when the element is tensioned.
Example: wire, cable, bar, rod, strand
- Tendon Anchor
-
A tendon anchor is the end connection for tendons in pre-stressed or post-tensioned concrete.
- Plate
-
A Plate is a planar and often flat part with constant thickness. A plate can be a structural part carrying loads between or beyond points of support, however it is not required to be load bearing. The location of the plate (horizontal, vertical or sloped) is not relevant to its definition.
- Discrete Accessory
-
A discrete accessory is a representation of different kinds of accessories included in or added to elements.
Example: visible steel corbel (corbel system made from steel components protruding from the master element), corner fixing plate (fixing plate attached to the corner of an element), steel plate (steel plate used as an accessory in a joint)
- Fastener
-
Representations of fixing parts which are used as fasteners to connect or join elements with other elements.
Example: jointing mortar, glue, weld
- Mechanical Fastener
-
Fasteners connecting building elements mechanically.
Example: bolt, screw, nail, nut, washer, rivet
Spatial Structure Elements
- Space
-
BIM Space entities from enclosed boundaries (3D solids or linear 2D entities).
- Building
-
Buildings in the model.
- Story
-
Story of the building / spatial elements.
Other Types (beta)
Information about each element type in this category can be found by accessing: https://standards.buildingsmart.org/IFC/RELEASE/IFC4/ADD2_TC1/HTML/annex/annex-b/en/alphabeticalorder_entities.htm