Mechanical Browser for Sheet Metal
Overview
The Mechanical Browser opens automatically when switching to the Mechanical workspace.
- Move the cursor over a toolbar, then right-click.
A context menu displays:
- Choose Mechanical Browser.
Sheet Metal Context
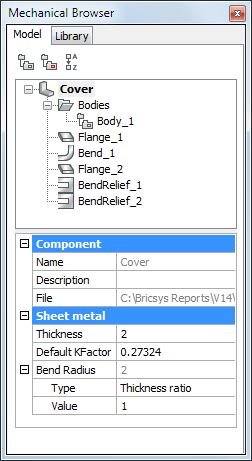
If you work with a sheet metal part (if you created any sheet metal feature), properties of the root node in Mechanical Browser contain Sheet Metal section (also called Sheet Metal Context associated with the document).
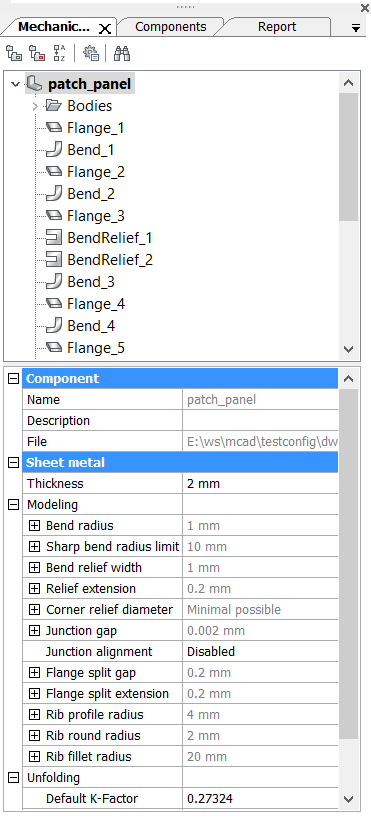
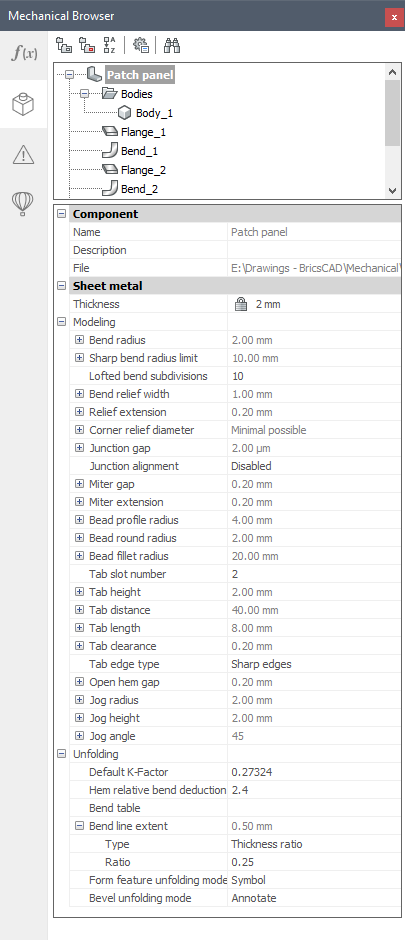
Sheet Metal properties are represented as grouped fields.
The Thickness field controls the material thickness of sheet metal solids.
- It provides default settings for Sheet Metal Commands, such as SMFLANGEBASE, SMEXTRUDE, SMFLANGEEDGE, SMFLANGEBEND, SMLOFT, and SMCONVERT in a newly created model. The initial parameters are saved in the drawing, which allows creating a set of .dwt template drawings for each type of sheet metal models created in a company.
- New features created by the commands usually derive their properties from Sheet Metal Context. For example, the default value of Radius Type property for the bend feature is "Use global value". Thus when you change Bend radius in Sheet Metal Context, all the bend features with the derived property will change its radius. So the second application of Sheet Metal Context properties is that they allow globally change properties of sheet metal part.
The Unfolding group of properties in Sheet Metal Context lists some properties of SMUNFOLD, SMEXPORT2D and SMASSEMBLYEXPORT commands.
Working with features
All features of a sheet metal part are listed in the Mechanical Browser. When you select a feature in the Mechanical Browser, its faces are highlighted in the model area:
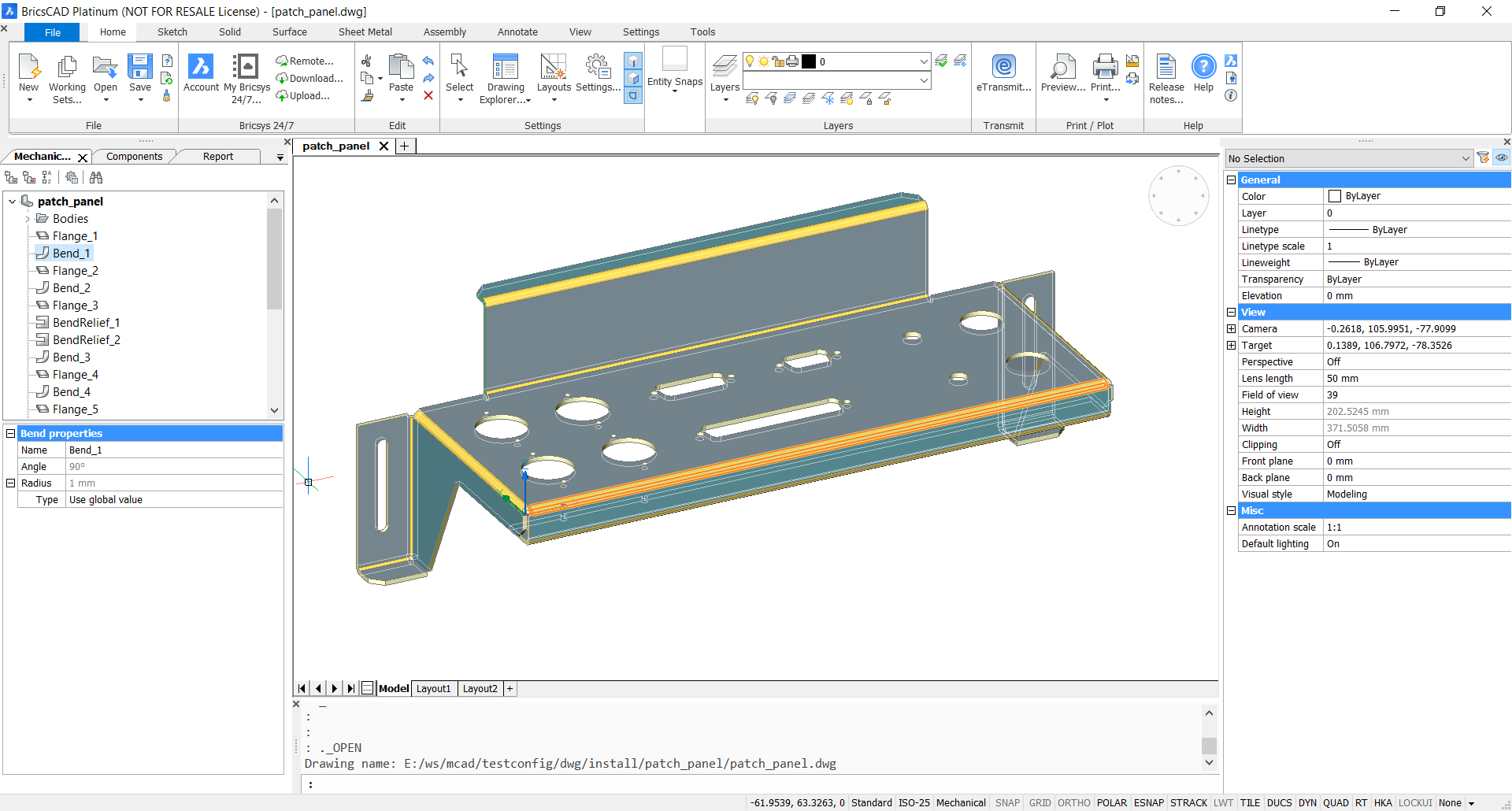
- Locate a feature on the part by highlighting its geometry.
- See the properties of given feature. For example, if you select a bend feature, Bend properties is displayed in the Mechanical Browser.
Changing the thickness
- Select the root node in the Mechanical Browser.
- Type a value in the Thickness field.
Feature operations
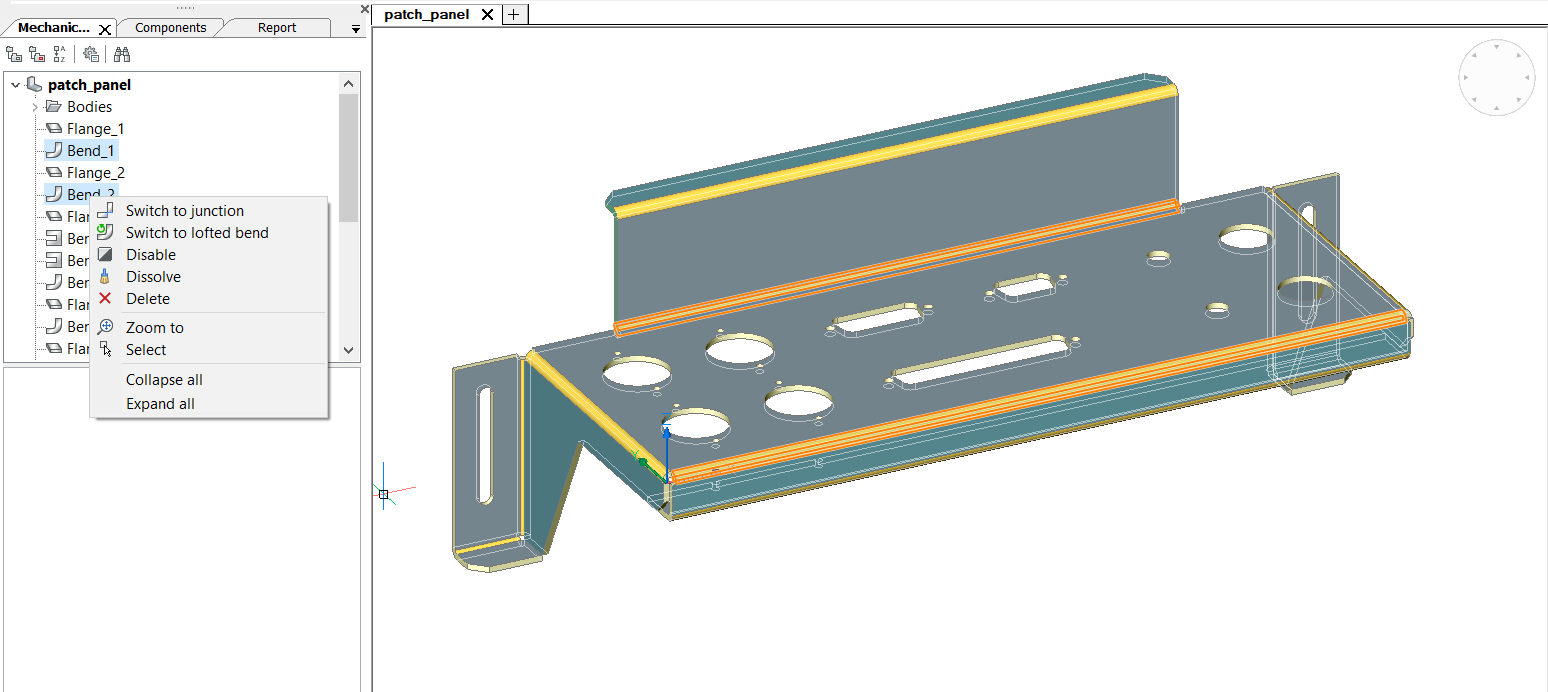
Mechanical Browser provides fast access to operations over given sheet metal feature, list depends upon the feature type. List of operations depends upon selected features and contains operations available for the selection.
Selecting 2 bends results in operations for bend feature:
Selecting flange and bend limits list to operations available for both features:
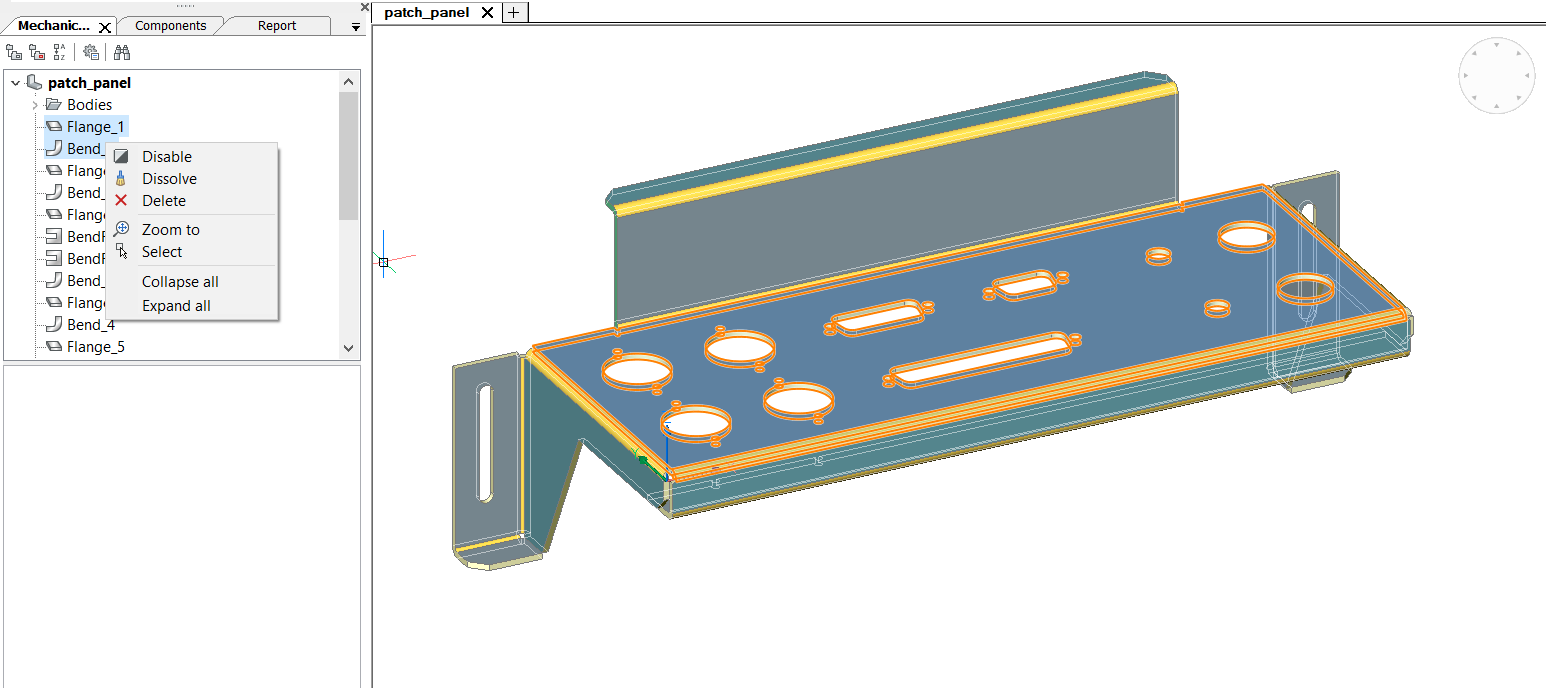
Understanding the difference between Disable, Dissolve and Delete
When you right-click a feature in the Mechanical Browser, then select Dissolve from the context menu the selected feature is removed from the part, but it will keep its geometry. However, design intent (spatial and parametric relationships between the feature’s faces) associated with the geometry of a dissolved feature is removed.
If your intent is temporary forget about given feature, you can choose Disable option. The feature will remain in the Mechanical Browser, but the part will behave like the feature was dissolved. It is beneficial in contrast with dissolve, that feature still updates on geometry changes and you can turn it on when you want, avoiding recreating it or recognizing by the SMCONVERT command.
Some of Sheet Metal features support Delete operation in the Mechanical Browser, which is the analogue of the SMDELETE command. In this case the feature is removed from the browser and geometry is changed depending upon the type of the feature.